This industry is usually influenced by multiple jurisdictions and supervised by different authorities, not to mention contractual regulation, so there are many things you should know when marketing your business. In this post, we present the key market players who might affect your campaign and the most important rules any affiliate must obey.
Who Are Key Market Players
Affiliate marketing regulations may vary for different niches and involve many legal questions. But, key market players and their responsibilities remain the same in every niche. We’ll start off with principal actors such as advertisers, affiliates, and affiliate networks, and then discuss the role of clients and governments.
Advertisers
Advertisers, also known as merchants or vendors, are companies that use affiliate marketing to promote their products. The terms set regarding traffic, content, and marketing strategies of affiliate websites is the first thing to comply with. Businesses are usually responsible for all claims made with respect to their product, that’s why they closely monitor affiliate activity.
Advertisers, in their turn, are regulated by local trade control organizations such as Federal Trade Control (FTC) and business associations like Better Business Bureau (BBB) in the United States.
Affiliate Networks
Affiliate networks are entities that connect advertisers and affiliates. They create platforms facilitating communication between both parties and provide needed support. Through networks, affiliates have access to multiple programs in a single interface and don’t have to approach each company separately, while advertisers can facilitate their communication with marketers.
Such networks are also regulated by trade organizations such as FTC and others.
By signing up with an affiliate network, publishers agree to follow its specific terms, which often concern the website quality and traffic. While Travelpayouts affiliate program registration is instant, some other platforms manually select affiliates and it might take longer to get approved.
Affiliates
Affiliates, also referred to as publishers and marketers, are the ones who drive traffic to advertisers’ websites. These can be bloggers, webmasters, online travel agents, social media influencers, and basically anyone with an online audience. While some affiliate programs require a website, in other cases you can become an affiliate even without your own blog.
Clients
Clients or customers are users who click on affiliate links and proceed to advertisers’ websites to perform the desired action. The thing you should always know about your audience is its geolocation as some advertisers have special requirements for the traffic.
Governments
Last but definitely not least, are governments. As an affiliate, you should pay attention to the legislation of both your country and the country (countries) of your customers regarding marketing, advertising, taxes, and more.
How to Make Your Affiliate Business Risk-Free
How can you make sure you’re complying with the most important rules of affiliate marketing and working risk-free? Carefully read through the following advice and follow it on every stage of your campaign promotion, from choosing an advertiser to reporting your income.
Choose Merchants Wisely
One of the main success factors for an affiliate is a choice of an advertiser to partner with. It is very important to conduct research and identify the following points:
- Product quality
- Merchant reputation and financial stability
- Terms and conditions of the offer
- Reviews of affiliates
Affiliate programs will only bring you sales if your audience find the products interesting, trustworthy, and relevant. While sticking with famous brands might seem like a good idea at first, it isn’t always the best solution, as their offers might not suit your target audience’s interests.
It’s also vital to check what kind of affiliate support you can get from an advertiser and/or affiliate network. For example, check out Travelpayouts’ tools review to learn about a wide array of promotional instruments available on the platform.
Many publishers prefer to test products themselves before recommending them to their readers because the reputation is more important. Moreover, when you pay for a product, your review is likely to be personal and authentic, which can largely contribute to the success of your campaign. In the travel niche, you can’t book an experience from an advertiser every time you want to promote them, but at least check the reviews of other affiliates.
Understand the Terms to Which You’re Agreeing
To get approved and be able to run your campaign for a long time, it’s crucial to review the offer terms, such as:
- Requirements for an affiliate (website traffic, content, etc.)
- Payment structure (model, commission, threshold, payment date, methods, etc.)
- Liability in case of legal issues
Advertisers usually require publishers to possess a website with a certain volume of traffic. It’s also important that the affiliate website is in the same niche with the advertiser’s products. Without complying with these criteria, you aren’t likely to be approved for a campaign.
Make sure you also understand the payment structure such as CPA or CPC model, affiliate commission, minimum amount for withdrawal, available payment methods, and other relevant details. While it is usually easier to generate clicks rather than sales, CPC affiliate programs offer lower commission, so try to find an advertiser that will suit your business and audience.
Finally, check liability limitations, which show whether the advertiser is required to reimburse you in case a client files a lawsuit, what happens if you fail to comply with the program rules, and so on. Inability to abide by the rules might get your account banned and commissions reversed.
Disclose Affiliate Links
From a regulation perspective, it’s vital to disclose any commercial relation you have with an advertiser. The rules vary depending on the country. For example, while the UK doesn’t provide any specific policy for the disclaimer, the Federal Trade Commission in the United States sets out particular recommendations:
- Users should be able to easily read the disclosure
- The wording of the disclosure should be understandable for readers
- It should be easy to spot on the page
- The disclosure should be close to the claim it makes
It is essential to comply with the legislation of the country your business is registered in and where your customers are based.
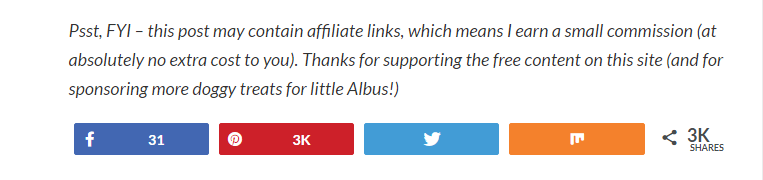
- Remember to disclose links in every post you’re using them. In the screen below, you can see a disclosure example from The Atlas Edit blog:
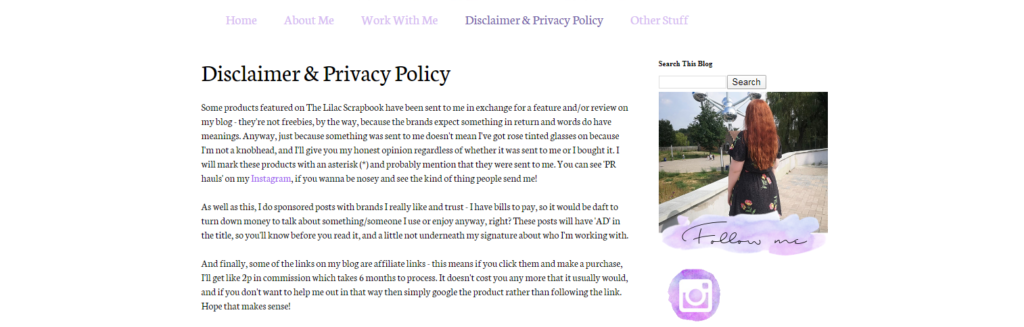
- Affiliate marketer Katy behind The Lilac Scrapbook blog includes disclosure in her Privacy Policy:
- Finally, some bloggers dedicate a separate page to list all the services they’ve used, likes and promote, as does the blogger behind The Nerdy Me blog:

Include a Privacy Policy
Uploading Privacy Policy on your website doesn’t only create trust between customers and the company, it is also legally required by governments and organizations around the world.
Thus, the EU Directive dictates that you must have a legal statement disclosing the privacy practices on your website in case you collect personal information of EU citizens. The GDPR requires you to ask for consent for handling data on a website or even including an agreement on the use of data collection and processing, mostly for cashback websites.
Another influential law — the CalOPPA — affects any business collecting data from California-based users, while the PIPEDA law controls data collection from Canada-based users and the Privacy Act of 1988 in Australia regulates data processing from Australian citizens. Given the internet omnipresence, there is a high chance some of your website visitors are from any of the abovementioned countries or states, so be sure to abide by the law.
Furthermore, some third-party services such as Google Analytics also require webmasters to upload a Privacy Policy disclosing the cookie usage. Google Ads also uses cookies for the purpose of remarketing and requires you to inform your website visitors about it.
What should a Policy include? You are to disclose the kind of personal data that you collect such as names, telephone numbers, email addresses, geolocation, IP addresses, payment details, etc. Moreover, make sure to state the purpose behind data collection, the way you collect it and any services that you share the data with. Finally, tell users how they can review and change the information that they’ve provided and how you’ll inform them of any changes in the policy.
Do you need a Privacy Policy if you don’t store any data? Some businesses prefer to upload such a policy in any case, even if it simply says that they don’t collect personal information.
What is the best place for a Privacy Policy? Most often, bloggers put it in the footer, and visitors are now used to looking for legal information at the bottom of the page, so you might want to follow this practice.
Comply With the Copyright
It is very important to also use only the content that you have rights to. This rule concerns texts, imagery, music, videos, and more. Create your own original content, use free content stocks or make purchases in photo banks.
Also, remember to use the advertiser’s brand name according to your affiliate agreement to avoid losing income or getting banned. For example, some merchants prohibit bidding on their name. Thus, be conscious about using trademarks of other companies in your domain name, content or meta tags. Quite a few marketers misuse other brands which creates negative effects for advertisers or networks.
Don’t Spam
Anti-spam laws protecting users from unsolicited emails are different for each country and email service provider, so make sure to familiarize yourself with the corresponding rules.
One of the most well-known laws is the CAN-SPAM Act of 2003. Here are its main requirements:
- Send newsletters only to those subscribers who have consented to receive it.
- Use only valid routing information such as your domain name and email address.
- Your email subject line should accurately represent the message.
- If your message is an ad, clearly state it.
- Include the valid physical address of your business.
- Include the “Unsubscribe” button or any other option to opt out of receiving your newsletter.
- Process an opt-out request fast.
- Keep an eye on all your contractors.
Beware of Marketing to Children
If you wish to promote any products geared towards children, be sure to obtain verified parental permission to collect, use, or disclose any personal information from children. Any promotion targeting young consumers is regulated by the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), enforced by the Federal Trade Commission.
Remember About Taxes
Last but not least is tax liability. Affiliate marketing implies referring customers to the advertiser and not selling products, creating a unique tax situation. There is no sole applicable regulation in this regard, as laws vary by country. Let’s consider the case of the U.S.-based affiliates:
- Most states exempt affiliates from sales tax as they receive income from referring customers and not sellings things.
- If your affiliate marketing company is incorporated, you must pay federal income tax.
- If you own a limited liability company, you’ll need to file an informational return and pay individual income tax.
- If the city you reside in has a city tax program, you’ll also pay city taxes.
- Affiliate marketers also have to pay self-employment taxes, which include Social Security and Medicare.
Naturally, regulation varies for each region, so be sure to familiarize yourself with the local laws.
Who Regulates Affiliate Marketing
While affiliate marketing might seem like a risky business at first, many affiliates around the world have already proven that with the right attitude, it is a trustworthy business.
The choice of the advertiser is half the battle, so start with the proper research of the market. Then, give due attention to reviewing the program terms and tax implications to prevent any nasty surprise in the future.
Finally, be sure to run your business in accordance with the applicable laws and keep informed about the industry and regulation changes.




